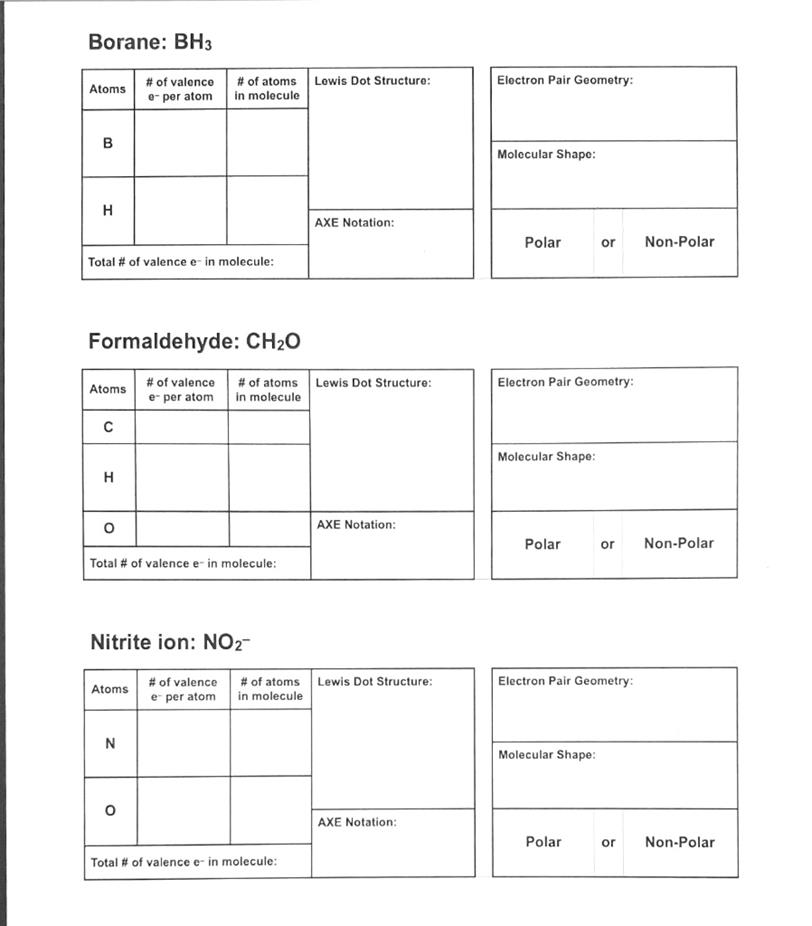
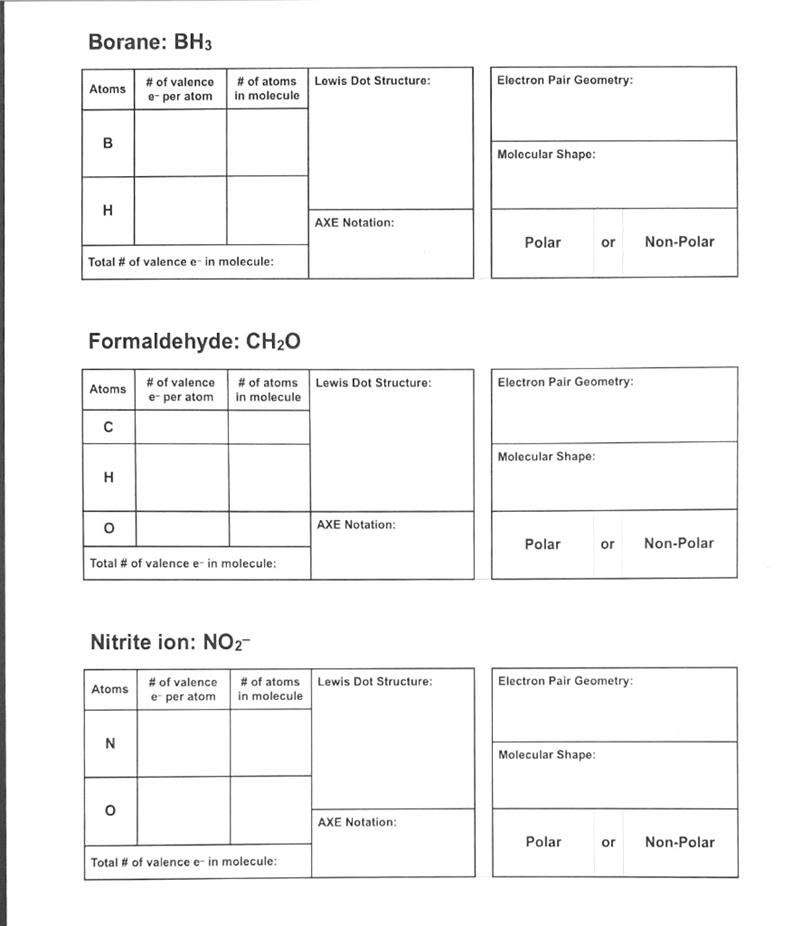
Borane: BH3 Lewis Dot Structure: Electron Pair Geometry: Atoms # of valence e- per atom # of atoms in molecule B Molecular Shape: H AXE Notation: Polar or Non-Polar Total # of valence e-in molecule: Formaldehyde: CH20 Atoms Lewis Dot Structure: Electron Pair Geometry: # of valence e per atom # of atoms in molecule ? Molecular Shape: H O AXE Notation: Polar or Non-Polar Total # of valence e-in molecule: Nitrite ion: NO2- Lewis Dot Structure: Electron Pair Geometry: Atoms # of valence e per atom # of atoms in molecule N Molecular Shape: AXE Notation: Polar or Non-Polar Total # of valence e-in molecule:

The Correct Answer and Explanation is :
Here are the answers to your questions along with a 300-word explanation.
1. Borane (BH₃):
- Lewis Dot Structure: Boron in the center with three single bonds to hydrogen atoms. Boron has an incomplete octet.
- Electron Pair Geometry: Trigonal planar.
- Atoms:
- Boron: 3 valence electrons.
- Hydrogen: 1 valence electron each (3 hydrogens = 3 electrons).
- Molecular Shape: Trigonal planar.
- AXE Notation: AX₃ (3 bonding regions, no lone pairs).
- Polar or Non-Polar: Non-polar (symmetrical charge distribution).
- Total # of Valence Electrons in Molecule: 6 (3 from Boron, 3 from Hydrogen).
2. Formaldehyde (CH₂O):
- Lewis Dot Structure: Carbon in the center bonded to two hydrogens and double-bonded to oxygen.
- Electron Pair Geometry: Trigonal planar.
- Atoms:
- Carbon: 4 valence electrons.
- Hydrogen: 1 valence electron each (2 hydrogens = 2 electrons).
- Oxygen: 6 valence electrons.
- Molecular Shape: Trigonal planar.
- AXE Notation: AX₃ (3 bonding regions, no lone pairs on carbon).
- Polar or Non-Polar: Polar (oxygen is more electronegative, causing a dipole moment).
- Total # of Valence Electrons in Molecule: 12 (4 from Carbon, 2 from Hydrogen, 6 from Oxygen).
3. Nitrite Ion (NO₂⁻):
- Lewis Dot Structure: Nitrogen is bonded to two oxygens, one with a single bond and one with a double bond. There is one lone pair on nitrogen and additional lone pairs on oxygens.
- Electron Pair Geometry: Trigonal planar.
- Atoms:
- Nitrogen: 5 valence electrons.
- Oxygen: 6 valence electrons each (2 oxygens = 12 electrons).
- Plus one extra electron for the negative charge.
- Molecular Shape: Bent (due to the lone pair on nitrogen).
- AXE Notation: AX₂E (2 bonding regions, 1 lone pair).
- Polar or Non-Polar: Polar (asymmetrical charge distribution).
- Total # of Valence Electrons in Molecule: 18 (5 from Nitrogen, 12 from Oxygen, 1 from the negative charge).
Explanation:
The geometry and polarity of molecules are determined using the VSEPR theory. Borane (BH₃) has no lone pairs on boron, leading to a symmetrical trigonal planar structure, making it non-polar. Formaldehyde (CH₂O) has a polar bond due to the electronegativity difference between oxygen and carbon, causing a dipole moment. The nitrite ion (NO₂⁻) has a bent shape because of the lone pair on nitrogen, making it polar. Calculating the total valence electrons helps confirm the correct structure, ensuring bonds and lone pairs are accounted for.